New Products and Features
Build smarter speech apps with real-time TTS
Turn text into a lifelike voice instantly. Telnyx real-time TTS API offers low latency, vendor flexibility, and support for 90+ languages.
Originally, text-to-speech (TTS) systems were developed to help people with visual impairments and learning disabilities like dyslexia interact more easily with digital content. These early systems made it possible for users to hear what was written on a screen turning digital text into spoken language in real time.
Today, TTS has grown far beyond its assistive roots. It now powers a wide range of everyday experiences, from interactive kiosks to in-game narration and voice-enabled customer service. The technology converts written text into synthetic speech, often using AI models to make that speech sound natural and responsive. Most modern TTS systems are offered as APIs, making it easy for developers to plug voice into their products.
According to a recent market report, the global TTS market was valued at $4 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $7.6 billion by 2029. That is a compound annual growth rate of 13.7% driven by AI advancements, accessible education initiatives, and the demand for natural-sounding, multilingual voice output in global markets.
Why text-to-speech is gaining ground
Several trends are converging to accelerate the adoption of TTS:
- AI-first voice synthesis is improving tone, clarity, and realism, making machine-generated voices more humanlike.
- Multilingual support is no longer a nice-to-have. Businesses need to communicate across borders, and TTS can scale content in many languages.
- Different use cases are emerging in education, media, healthcare, and accessibility pushing TTS into new environments where personalized audio is more useful than written content.
- Low-latency APIs are making real-time speech output viable in applications like chatbots, live assistants, and voice-controlled interfaces.
Practical use cases of text-to-speech across industries
Here’s a closer look at how different industries are applying TTS to improve usability, efficiency, and accessibility:

1. AI companions and virtual assistants
From Siri to enterprise phone systems, TTS gives machines a voice. When combined with speech recognition, virtual assistants can hold responsive conversations, read notifications aloud, and handle repetitive tasks in natural, humanlike ways.
2. Accessibility and assistive tech
TTS helps users with visual impairments or mobility limitations by reading on-screen content, messages, and notifications in real time. It powers screen readers and caption-to-speech tools that keep pace with live content, making interfaces more inclusive.
3. Customer experience kiosks
Interactive touchscreens in retail, airports, healthcare, and banking environments rely on real-time voice prompts that adapt to user input and backend data. TTS enhances the experience by replacing static menus with conversational guidance.
4. Meditation and wellness apps
These apps generate real-time affirmations or guided meditations that change based on user behavior, preferences, or time of day. TTS allows them to deliver personalized voice content without manual recording or scheduling.
5. E-learning and interactive education
TTS reads lessons, quizzes, and feedback aloud in real time, adjusting tone and content as students interact. It supports attention, comprehension, and accessibility, making learning platforms more adaptive and engaging.
6. Navigation systems
GPS and mapping apps use TTS to vocalize dynamic instructions, like street names or detour routes on the fly. Real-time synthesis makes directions clear and personalized, especially in multilingual or fast-changing environments.
7. Multilingual communication and translation
TTS bridges language gaps by vocalizing translations in real time. Apps like interpreters or AI agents can speak to users in their preferred language, using natural prosody and accent-appropriate voices.
8. Enterprise and contact center automation
Voicebots powered by TTS can answer calls, guide users through menus, and deliver notifications. Real-time speech ensures faster service without needing pre-recorded prompts.
9. Media and entertainment
Game studios and content creators use TTS to generate scalable voiceovers, including dynamic in-game dialogue, AI narration, and localized versions of content. News sites and blogs also use TTS to instantly convert published articles into spoken updates.
While some of these applications can be handled with non–real-time TTS, such as pre-generating audio files for media or eBooks, many now require speech output the moment text is created. In such cases, real-time speech keeps interactions fluid and natural.
Real-time text-to-speech
As the demand for instant, natural communication grows, real-time TTS has become a critical part of modern voice experiences. Developers need tools that can generate lifelike speech the moment it’s needed, whether that’s in a live call, a chatbot response, or a mobile interaction.
Telnyx built its TTS API specifically for that need. It’s powered by the same low-latency global network that supports our Voice API, allowing developers to create seamless speech interactions inside or outside of a call environment.
A single API with complete voice flexibility
With Telnyx, developers don’t have to lock into a single vendor. Our TTS API gives you access to Telnyx-native voices as well as AWS Polly and Azure voices, all through one integration. That means you can:
- Experiment with tone and clarity across vendors
- Combine speakers and languages in the same session
- Localize content in over 90 languages and regional variants without extra complexity
This flexibility is especially powerful for applications that need to switch voices mid-session, adapt to user preferences, or operate across regions. Watch this demo to see our voice options.
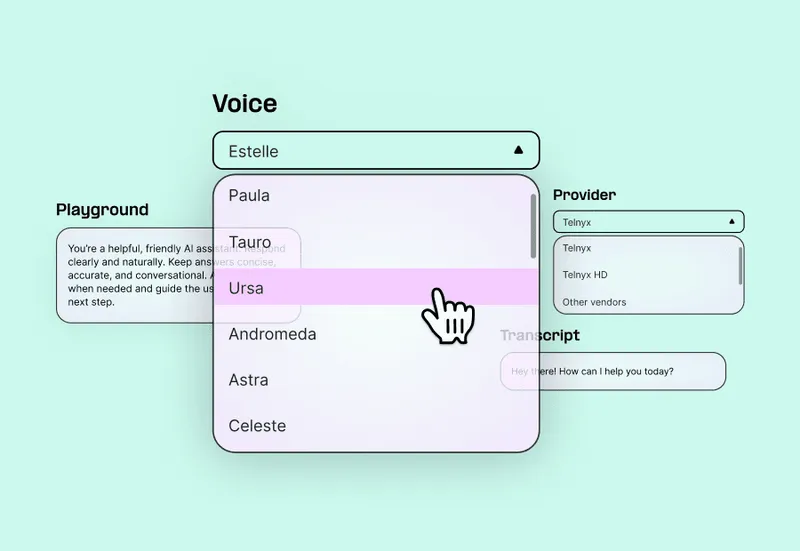
Designed for real-time performance
Telnyx’s real-time TTS delivers low-latency speech that starts streaming the moment text is generated. Dynamic voice control allows you to change tone, accent, or even speaker mid-session, ideal for complex or multilingual flows.
Built to scale globally and affordably
From startup experiments to enterprise-scale deployments, pricing should never be a blocker. Telnyx offers competitive per-character pricing with no hidden fees. You only pay for what you use, and you can balance quality and cost by choosing from multiple voice types depending on the use case. Our global reach means you can deploy voice experiences anywhere from day one. With native support for more than 90 languages, and delivery over our private global IP network, Telnyx ensures consistent quality and coverage wherever your users are.
Start building with real-time TTS. Talk to our team to get started.
Have questions about real time TTS? Join our subreddit.
Share on Social
Sign up for emails of our latest articles and news
Related articles
